|
Scientific Name | Tritonia cooperi (Baker) Klatt subsp. cooperi |
Higher Classification | Monocotyledons |
Family | IRIDACEAE |
Synonyms | Gladiolus longiflorus L.f. (in part), Ixia cooperi Baker, Morphixia cooperi Baker, Tritonia longiflora N.E.Br. (in part), not of Ker Gawl. (1804), Tritonia longituba R.C.Foster (in part) |
National Status |
Status and Criteria | Least Concern |
Assessment Date | 2021/07/05 |
Assessor(s) | W. Foden, L. Potter & T. Patel |
Justification | This taxon has an extent of occurrence (EOO) of 137 798 km², and an area of occupancy (AOO) of 88 km². It is known from between 18 and 22 subpopulations. The species is currently assessed as Least Concern as it is too abundant to be at risk of extinction in the near future, however the population trends should be monitored. |
Distribution |
Endemism | South African endemic |
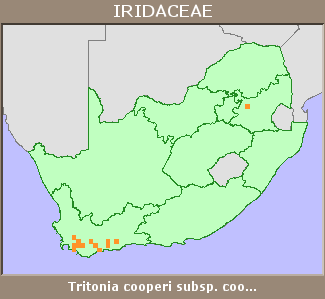
Provincial distribution | Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Western Cape |
Range | It is endemic to South Africa, and is found on the coastal plain and mountains of Western Cape, from Du Toit's Kloof to Kogelberg and east across the Riviersonderend Mountains and Langeberg to Riversdale and the Potberg. Recent records place this subspecies in KwaZulu-Natal. |
Habitat and Ecology |
Major system | Terrestrial |
Major habitats | Fynbos, Succulent Karoo |
Description | Plants grow on sandstone slopes in fynbos, flowering well after fire. |
Threats |
| This taxon has lost 46% suitable habitat (calculated using landcover data on GIS) within its range due to infrastructural developments and habitat degradation from livestock and competition from invasive alien species. This species is also being illegally collected for the medicinal trade. |
Population |
It is known from between 18 and 22 subpopulations, and it has a stable population trend.
|
Population trend | Stable |
Assessment History |
Taxon assessed |
Status and Criteria |
Citation/Red List version | | Tritonia cooperi (Baker) Klatt subsp. cooperi | Least Concern | Raimondo et al. (2009) | |
Bibliography |
Goldblatt, P. and Manning, J.C. 2020. Iridaceae of southern Africa. Strelitzia 42. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria.
Raimondo, D., von Staden, L., Foden, W., Victor, J.E., Helme, N.A., Turner, R.C., Kamundi, D.A. and Manyama, P.A. 2009. Red List of South African Plants. Strelitzia 25. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria.
|
Citation |
| Foden, W., Potter, L. & Patel, T. 2021. Tritonia cooperi (Baker) Klatt subsp. cooperi. National Assessment: Red List of South African Plants version 2024.1. Accessed on 2026/02/14 |
 Comment on this assessment
Comment on this assessment