| Scientific Name | Cotula filifolia Thunb. | Higher Classification | Dicotyledons | Family | ASTERACEAE |
National Status | Status and Criteria | Near Threatened B2ab(ii,iii,iv,v) | Assessment Date | 2013/10/22 | Assessor(s) | R.F. Powell, N.A. Helme & L. von Staden | Justification | A widespread (EOO 36 295 km²), but localized habitat specialist (AOO <2000 km²), that is still fairly common, estimated to occur at between 20 and 25 remaining locations. This species is however declining due to ongoing habitat loss to coastal development in particular, and is also threatened by competition from unmanaged alien invasive plants and habitat loss and degradation as a result of agricultural expansion. |
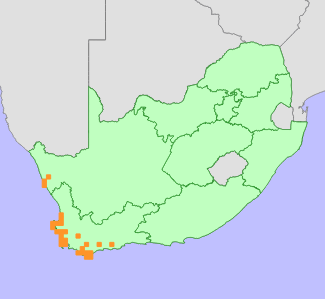
Distribution | Endemism | South African endemic | Provincial distribution | Northern Cape, Western Cape | Range | Cape West Coast, from Hondeklipbaai to the Cape Peninsula, and also on the Agulhas Plain. |
Habitat and Ecology | Major system | Freshwater | Major habitats | Eastern Ruens Shale Renosterveld, Hopefield Sand Fynbos, Atlantis Sand Fynbos, Cape Flats Sand Fynbos, Hangklip Sand Fynbos, Agulhas Sand Fynbos, Albertinia Sand Fynbos, Swartland Granite Renosterveld, Breede Alluvium Fynbos, Central Ruens Shale Renosterveld, Namaqualand Coastal Duneveld, Swartland Shale Renosterveld, Saldanha Granite Strandveld, Saldanha Limestone Strandveld, Langebaan Dune Strandveld, Cape Flats Dune Strandveld, Overberg Dune Strandveld, Namaqualand Heuweltjieveld, Namaqualand Strandveld, Western Ruens Shale Renosterveld | Description | Marshy ground, pools and damp places. |
Threats | | Cotula filifolia is widespread and still fairly common, and has declined most extensively on the Cape Peninsula, where most subpopulations known from historical records are now locally extinct due to habitat loss to urban expansion. Along the Cape West Coast, many subpopulations are threatened by habitat loss to coastal development, and further inland, around Darling, very little of this species' former habitat remains due to extensive modification for crop cultivation. On the Agulhas Plain, in addition to habitat loss to coastal development, many subpopulations are also threatened by competition from alien invasive plants. |
Population | A widespread species, and locally common in suitable habitat.
| Population trend | Decreasing |
Assessment History |
Taxon assessed |
Status and Criteria |
Citation/Red List version | | Cotula filifolia Thunb. | NT B2ab(ii,iii,iv,v) | 2014.1 | | Cotula filifolia Thunb. | CR B2ab(ii,iii,v) | 2013.1 | | Cotula filifolia Thunb. | CR B2ab(ii,iii,v) | Raimondo et al. (2009) | |
Bibliography | Cook, C.D.K. 2004. Aquatic and wetland plants of southern Africa. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands.
Goldblatt, P. and Manning, J.C. 2000. Cape Plants: A conspectus of the Cape Flora of South Africa. Strelitzia 9. National Botanical Institute, Cape Town.
Powell, R.F., Boatwright, J.S. and Magee, A.R. 2014. A taxonomic revision of the Cotula coronopifolia group (Asteraceae) and implications for the conservation statuses of the species. South African Journal of Botany 93:105-117.
Raimondo, D., von Staden, L., Foden, W., Victor, J.E., Helme, N.A., Turner, R.C., Kamundi, D.A. and Manyama, P.A. 2009. Red List of South African Plants. Strelitzia 25. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria.
Sieben, E.J.J. 2009. The status and distribution of vascular plants (Magnoliophyta, Lycophyta, Pteridophyta). In: W.R.T. Darwall, K.G. Smith, D. Tweddle and P. Skelton (eds.), The status and distribution of freshwater biodiversity in southern Africa (pp. 83-98), IUCN and SAIAB, Gland, Switzerland and Grahamstown, South Africa.
|
Citation | | Powell, R.F., Helme, N.A. & von Staden, L. 2013. Cotula filifolia Thunb. National Assessment: Red List of South African Plants version 2024.1. Accessed on 2026/03/03 |
 Comment on this assessment Comment on this assessment
|
 © N.A. Helme
Search for images of Cotula filifolia on iNaturalist
|
 Comment on this assessment
Comment on this assessment