|
Scientific Name | Grewia pondoensis Burret |
Higher Classification | Dicotyledons |
Family | MALVACEAE |
Common Names | Pondo Cross-berry (e) |
National Status |
Status and Criteria | Near Threatened B1ab(iii,v)+2ab(iii,v) |
Assessment Date | 2007/11/27 |
Assessor(s) | L. von Staden & A.T.D. Abbott |
Justification | EOO 2800 km², AOO<50 km², known from more than 10 locations, and subpopulations are not severely fragmented. The quality and extent of this species' habitat, and number of mature individuals is declining as a result of too frequent and intense grassland fires, harvesting for firewood and building materials, and alien plant invasion. |
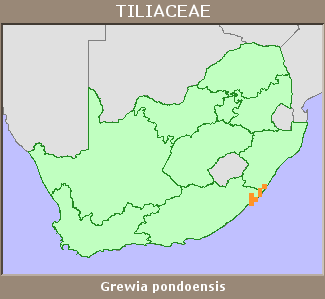
Distribution |
Endemism | South African endemic |
Provincial distribution | Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal |
Range | Oribi Gorge to Port St Johns. |
Habitat and Ecology |
Major system | Terrestrial |
Major habitats | Eastern Valley Bushveld, Scarp Forest, Pondoland-Ugu Sandstone Coastal Sourveld, KwaZulu-Natal Coastal Belt Grassland |
Description | Pondoland scarp forest on Msikaba Formation Sandstone, in forest margins, cliffs and rocky places, 100-500 m. |
Threats |
| The main threats to Pondoland woody endemics restricted to forest margins are too frequent and intense grassland fires that are causing forest margins to recede (D. Styles, C.R. Scott-Shaw pers. obs.) as well as the indiscriminate harvesting of wood for fuel and building materials (T. Abbott pers. comm.) G. occidentalis, a very similar species, is known to have hard wood that is favoured for use as sticks and spear shafts (Pooley 1998).
These threats are affecting forest margins mainly in the areas between Umtamvuna and Mkambati Nature Reserves, as well as between Mkambati and Port St Johns.
From Port Edward to Oribi the largest remaining areas of forest are fairly well protected within the Umtamvuna and Oribi Gorge Nature Reserves, however, some areas of forest above the edges of these deep gorges have undoubtedly been cleared for forestry and agriculture (mainly sugarcane) in the past.
Smaller forest patches outside of reserves are threatened by the effects of fragmentation and isolation within a transformed landscape as well as alien invasive encroachment. |
Population |
Population trend | Decreasing |
Assessment History |
Taxon assessed |
Status and Criteria |
Citation/Red List version | | Grewia pondoensis Burret | NT B1ab(iii,v)+2ab(iii,v) | Raimondo et al. (2009) | | Grewia pondoensis Burret | Lower Risk - Least Concern | Scott-Shaw (1999) | | Grewia pondoensis Burret | Rare | Hilton-Taylor (1996) | |
Bibliography |
Boon, R. 2010. Pooley's Trees of eastern South Africa. Flora and Fauna Publications Trust, Durban.
Hilton-Taylor, C. 1996. Red data list of southern African plants. Strelitzia 4. South African National Botanical Institute, Pretoria.
Raimondo, D., von Staden, L., Foden, W., Victor, J.E., Helme, N.A., Turner, R.C., Kamundi, D.A. and Manyama, P.A. 2009. Red List of South African Plants. Strelitzia 25. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria.
Scott-Shaw, C.R. 1999. Rare and threatened plants of KwaZulu-Natal and neighbouring regions. KwaZulu-Natal Nature Conservation Service, Pietermaritzburg.
|
Citation |
| von Staden, L. & Abbott, A.T.D. 2007. Grewia pondoensis Burret. National Assessment: Red List of South African Plants version 2024.1. Accessed on 2025/12/23 |
 Comment on this assessment
Comment on this assessment